数值分析实验之非线性方程求根(Python 现)
2021-01-16 10:15
标签:NPU def split 牛顿迭代 技术 range point lang psi 详细实验指导见上一篇,此处只写内容啦 实验内容: 1. 用二分法求方程x3-3x-1=0在的所有根.要求每个根的误差小于0.001. 提示与要求: (1) 利用精度找到迭代次数; (2) 由f(x)=3(x2-1)可取隔根区间[-2,-1].[-1,1].[1,2]); (3) 用程序求各隔根区间内的根. 2. 用不动点迭代求: (1)x3+2x2+10x-20=0的所有根. 或: (2)9x2-sinx-1=0在[0,1]上的一个根. 3. 用Newton迭代法求解下列之一,准确到10-5: (1) x3-x-1=0的所有根; (2) ex+2-x+2cosx-6=0位于[0,2]上的根. 实验代码: • 牛顿迭代法 运行结果: • 不动点法 运行结果: 数值分析实验之非线性方程求根(Python 现) 标签:NPU def split 牛顿迭代 技术 range point lang psi 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ynly/p/12894247.html 1 import math
2 x=0.5
3 n = 1
4 while n ==1 or abs(x-x1)>1e-5:
5 x1 = x
6 def F(x1):
7 return 2**-x+2*math.cos(x)+math.exp(x)-6
8 def F1(x1):
9 return math.exp(x)-math.log(2)*(2**-x)-2*math.sin(x)
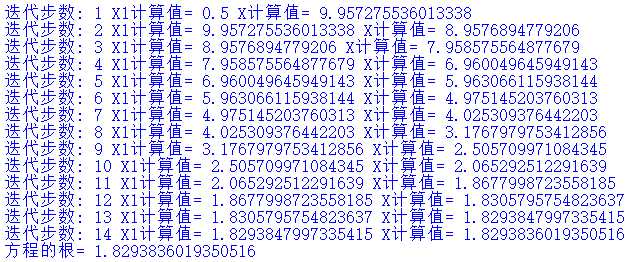
10 x = x1 - F(x1)/F1(x1)
11 print (‘迭代步数:‘,n,‘X1计算值=‘,x1,‘X计算值=‘,x)
12 n = n+1
13 else:
14 print(‘方程的根=‘,(x))
1 import numpy as np
2
3 def f(x):
4 return 9*x**2 - np.sin(x) - 1
5
6 def g1(x):
7 return ((np.sin(x)+1)/9)**0.5
8
9 def g2(x):
10 result = (abs(2 * x + 1))**(1 / 5)
11 if (2 * x - 1) 0:
12 return -result
13 return result
14
15 def getEpsilon(x, epsilon):
16 maxY = minY = x[0]
17 for each in x:
18 maxY = max(f(each), maxY)
19 minY = min((f(each), minY))
20 epsilon = (maxY - minY) * epsilon
21 return epsilon
22
23 def getInitialVal(x, N, step, epsilon):
24 initalVal = []
25 for i in range(N + 1):
26 y1, y2, y3 = f(x - step), f(x), f(x + step)
27 if (y1 * y2 and (i != 0):
28 initalVal.append((x + x - step) / 2)
29 if ((y2 - y1) * (y3 - y2) and (abs(y2) epsilon):
30 initalVal.append(x)
31 x += step
32
33 return initalVal
34
35 def findFixedPoint(initalVal, delta,epsilon):
36 points = []
37 for each in initalVal:
38 if (abs(g1(each)) ):
39 points.append(iteration(each, g1, delta,epsilon))
40 else:
41 points.append(iteration(each, g2, delta,epsilon))
42 return points
43
44 def iteration(p1, g, delta,epsilon):
45 while True:
46 p2 = g(p1)
47 err =abs(p2-p1)
48 relerr = err/(abs(p2)+epsilon)
49 if err
![]()
上一篇:java--面向对象重点
下一篇:python-装饰器